Workflow Extensions for a HumanTask
Overview
CaseFabric provides for a series of extensions to the CMMN HumanTask in order to support enhanced workflow handling.
- Workflow lifecycle extensions (like claim and delegate)
- Applying Workflow at design time
- Role based authorizations
- Setting due dates on Human Tasks
- Dynamic assignment of Human Tasks to users
- Workflow patterns for Rendez-Vous and Four-Eyes
- Reusable HumanTask implementations
- Human Task rendering in CaseFabric UI
- Dealing with Task Data
- Mandatory Task output parameters
- Storing, Validating and Completing with Task output
Lifecycle Extensions
In CMMN, a task and stage have a predefined set of states to support the lifecycle, with Available, Active and Completed as the primary states.
Task input is set when a task becomes Active.
In typical workflow scenarios, it may be necessary to know whether a task is already picked up by someone, or to delegate a task to someone else if we're too busy.
CaseFabric Engine adds a few states to a Human Task in Active state. We can consider them 'sub states'. They do not have any effect in the Case Plan, but merely help in querying tasks.
These states are stored in a custom field taskState to avoid confusion with the normal CMMN lifecycle.
Furthermore, CaseFabric stores an owner and an assignee for each HumanTask.
Note that the extra lifecycle steps are optional. E.g. a user with the proper authorizations can complete a task without claiming it.
Lifecycle operations
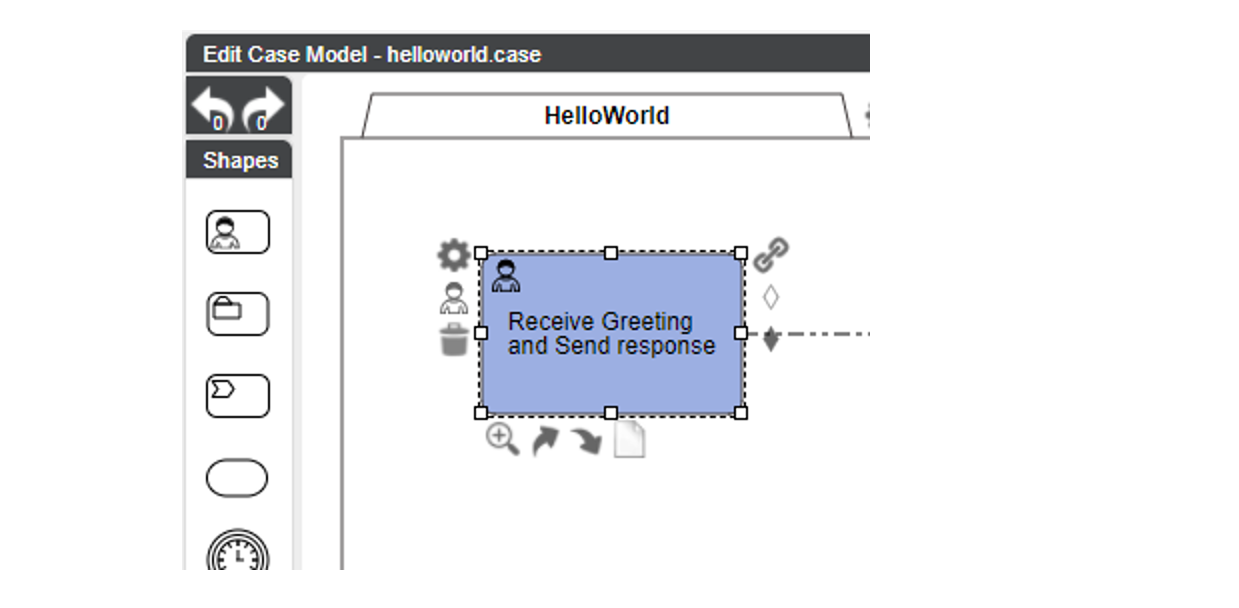
When a task becomes Active, it is in sub-state Unassigned. It can then be claimed by or assigned to team members with appropriate authorization.
If a task is claimed by a user (or assigned to a user), that user becomes both owner and assignee, and the task goes into sub-state Assigned.
When the user delegates the task to another user, the initial user is still the owner, but the other user becomes the assignee. The task goes into sub-state Delegated.
This process can be reverted through the revoke action.
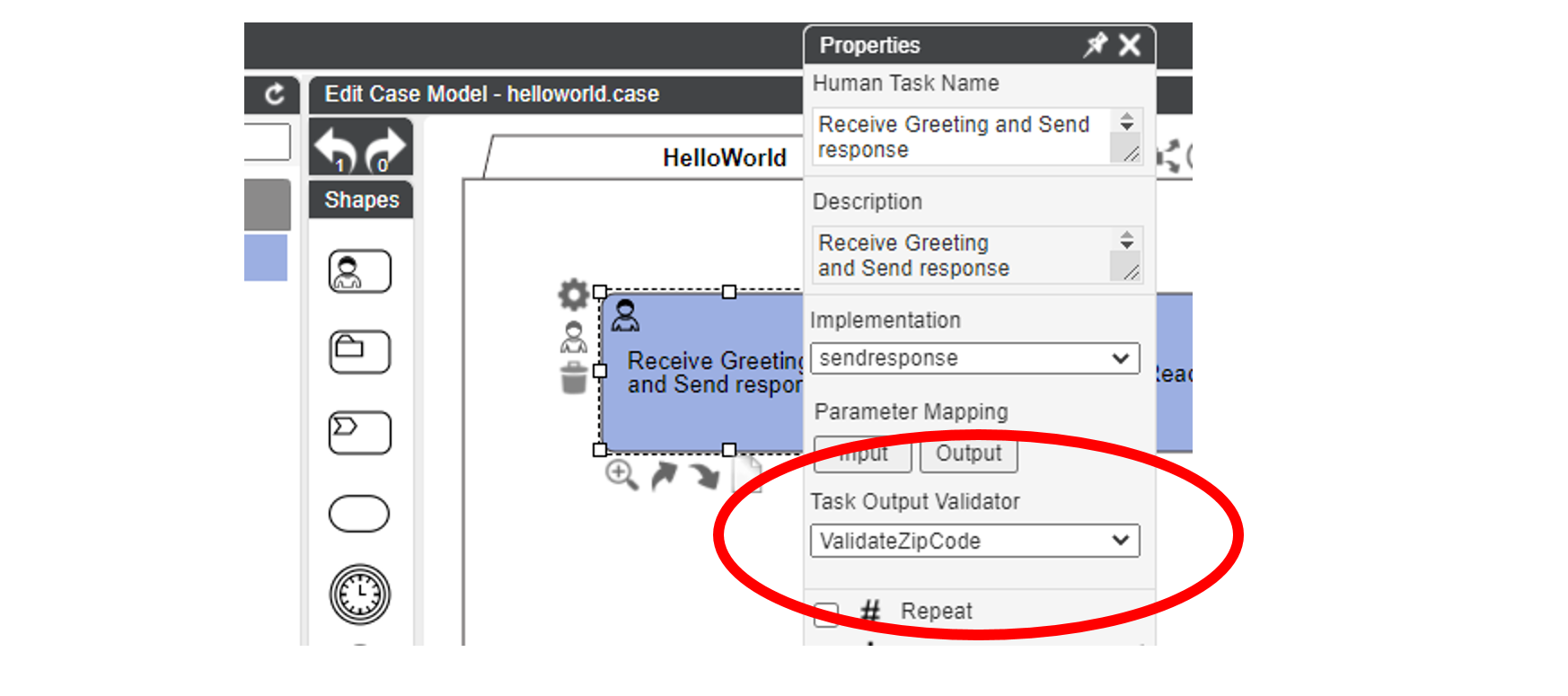
Workflow Properties
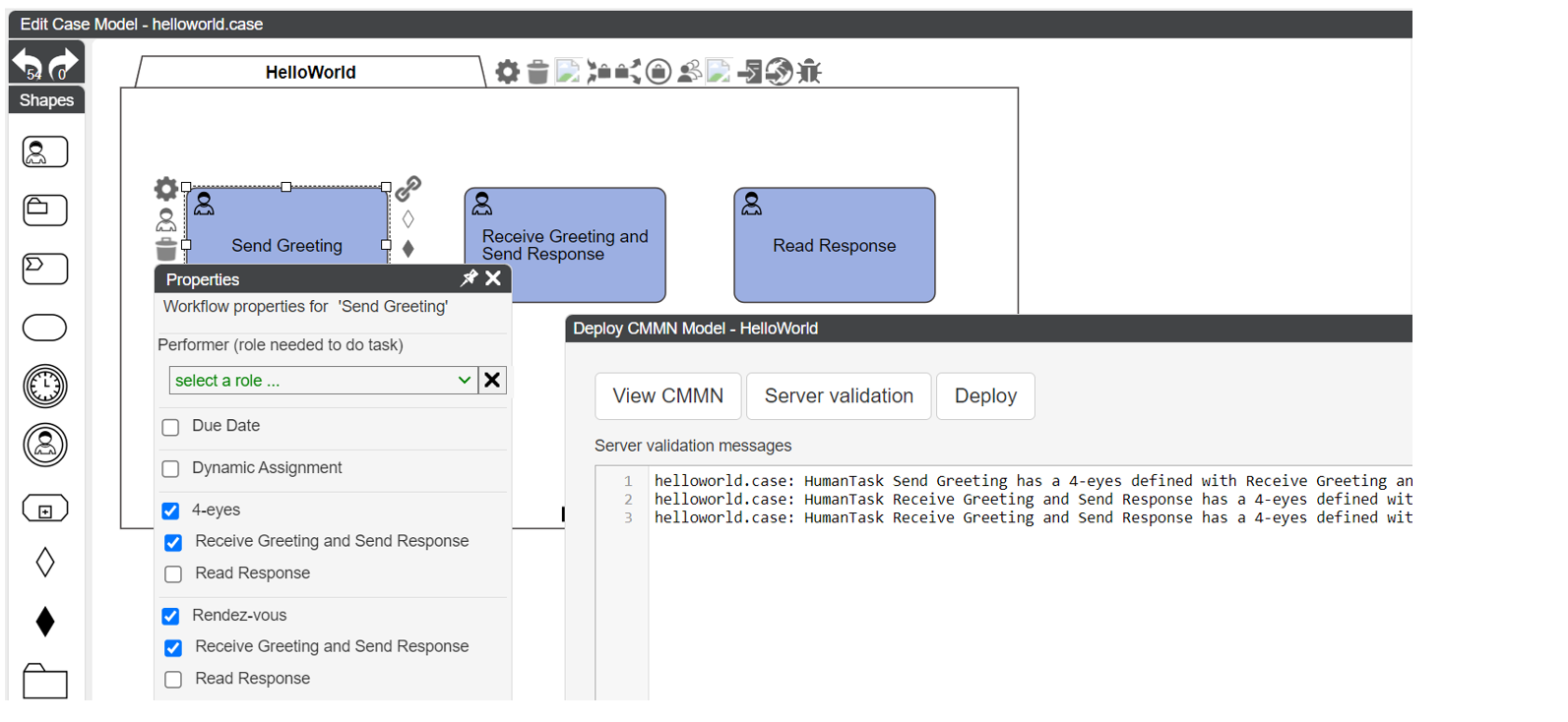
The image shows the available options to implement and extend the CMMN Human Task described below.
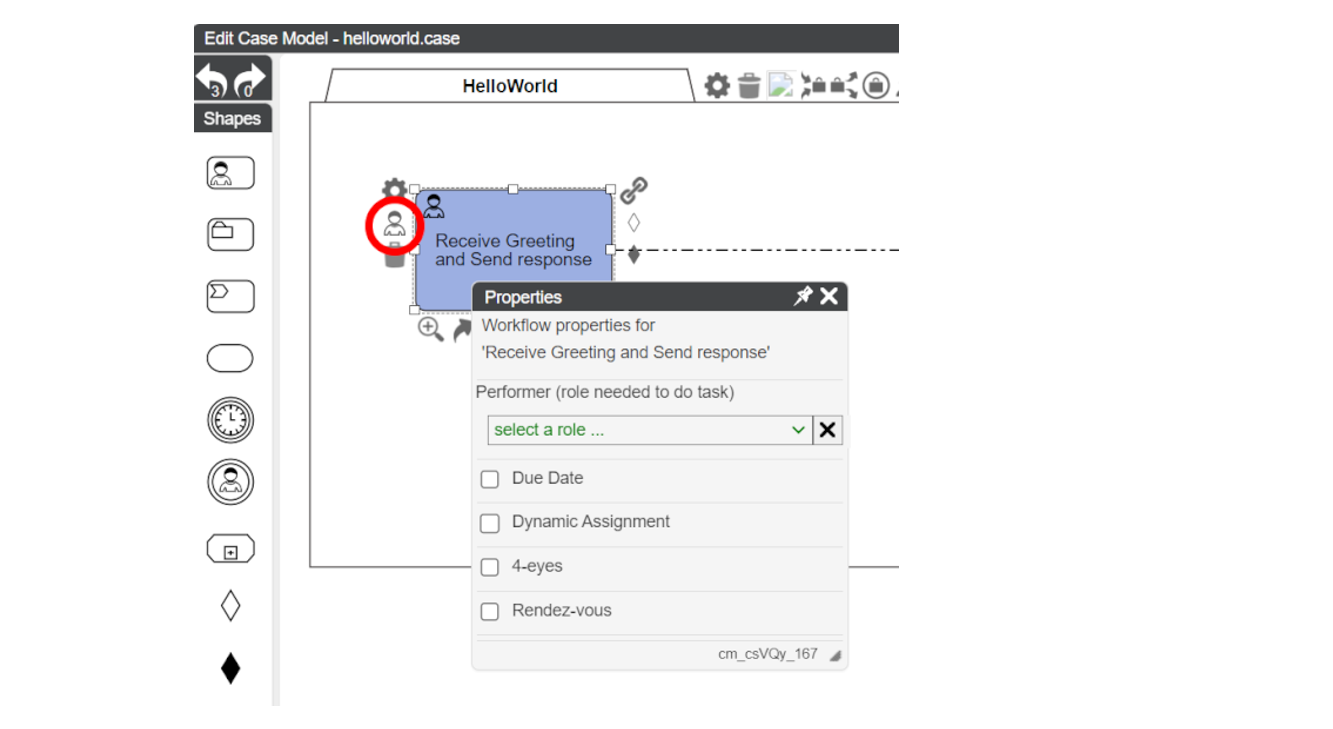
Performer role is defined in CMMN.
Due Date, Dynamic Assignment, 4-eyes and Rendez-Vous are CaseFabric extensions.
CMMN Performer Role
CMMN supports Human Task Authorization through the notion of the "Performer" role.
Setting this role implies that the Human Task is only available for members of the case team with that role.
Note: authorizations are managed by case owners.
Case owners can directly override actions on tasks. This includes e.g. revoking assigned tasks or directly completing a task that is currently assigned to another user.
Due Date
The due date of a Human Task can be filled through an expression.
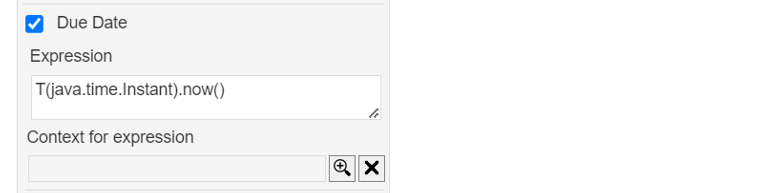
The expression is evaluated in the optional context of a Case File Item, similar to other expressions in CMMN.
Due date does not imply any behavior in the case engine. It is merely a date/time field that is passed on to the query database, where it can be used to select, filter and sort tasks.
Dynamic Assignment
Upon activating a task, it can be directly assigned to a specific user through an expression.
This option can be used in addition to the REST API for assigning tasks.

Note: task assignment (or delegation) does not validate user existence.
Authorization consequences
It is important to realize that the CaseFabric Engine tries to validate the existence of the user id, but it allows for unrecognized user ids. The reason for this, is that the user identification is not up to CaseFabric, but to the IDP that CaseFabric trusts.
Assignment and delegation will not just assign the task to the user id passed. The engine will also verify that whether user id is already in the case team, and, if not, the user id will be added. Note that assignment and delegation through the API can only be done by case owners - and they have the rights to manage the case team. If the user is added to the case team, this will be only with the performer role that is congfigured on the task.
Dynamic task assignment is done through the model definition, and can therefore also be triggered by case team members that do not have case ownership.
Four-Eyes and Rendez-Vous principle
In order to more easily explain the typical workflow patterns Four-Eyes and Rendez-Vous we use a somewhat modified version of the Hello World case.
The first task in the case, is to compose and send the greeting. The second task is to receive it and reply to it. And the third task is to read the reply.

Obviously, the second task is to be done by someone else than the person sending the greeting. And, reading the response is to be done by the person that originally sent the greeting.
The workflow patterns Four-Eyes and Rendez-Vous can enforce this.
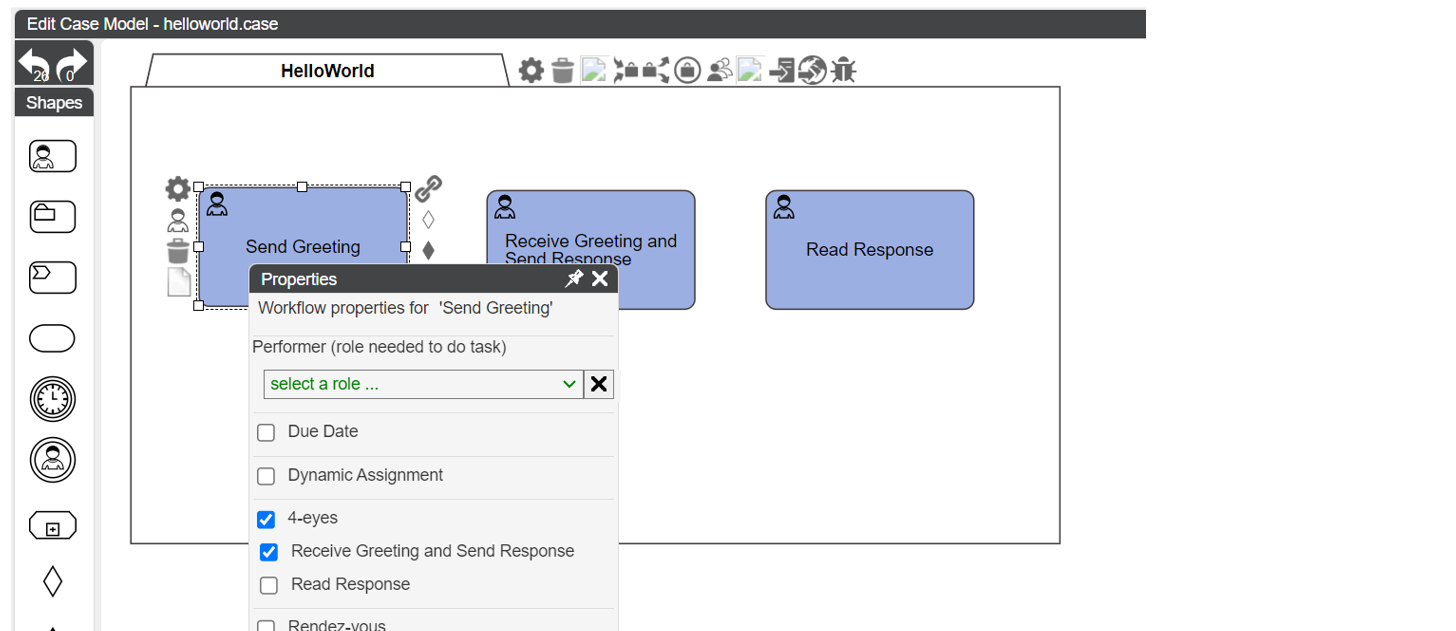
Four Eyes
In the Four Eyes configuration, we can ensure that 2 tasks are performed by 2 different users.
The below checkbox indicates that the tasks "Send Greeting" and "Receive Greeting and Send Response" must be performed by 2 different users.
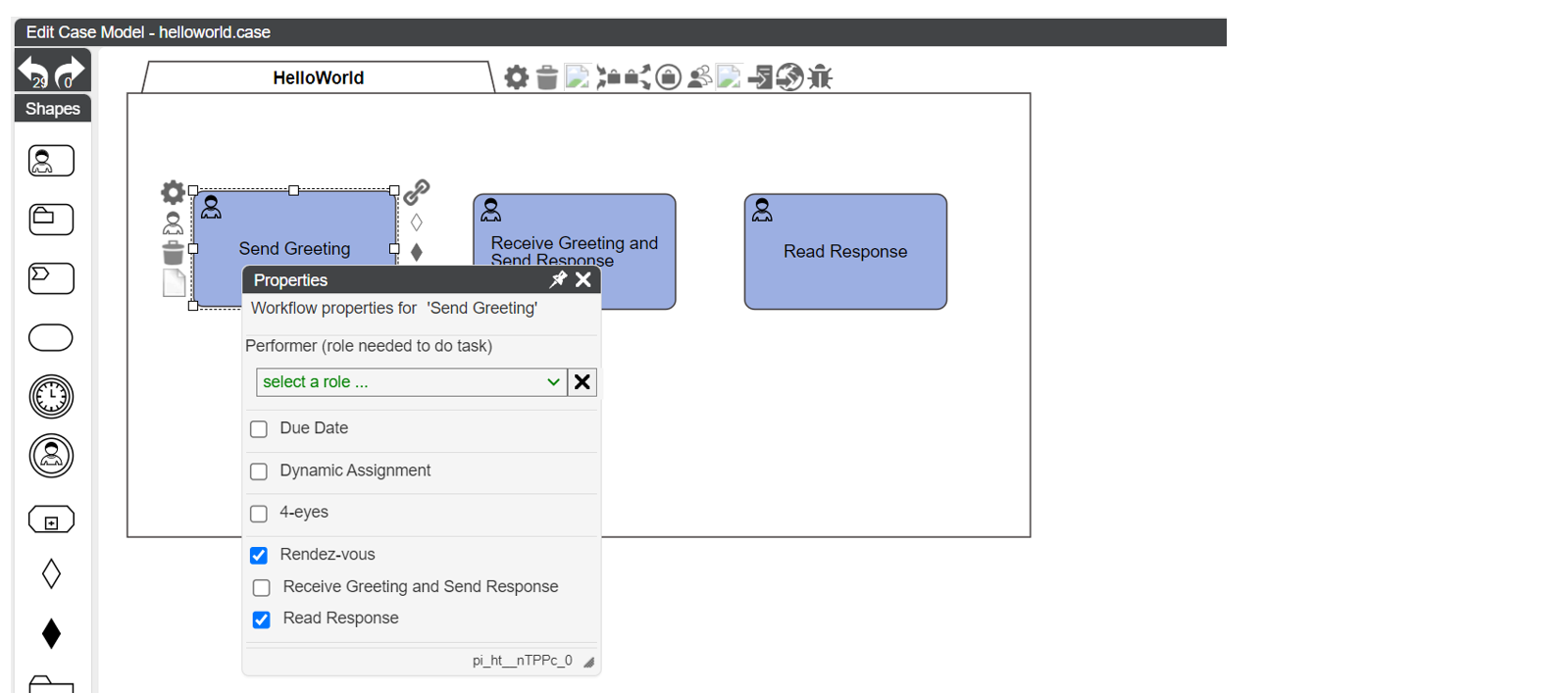
Rendez Vous
Through Rendez Vous, the opposite of Four Eyes can be enforced: 2 tasks are to be performed by the same user.
Combining Rendez Vous and Four Eyes
It is possible to combine Rendez Vous and Four Eyes. The properties of the above 2 examples can be combined. This would enforce the same user to handle the first and last task, and the second task must be performed by someone else.
Combining both options on tasks can be used to implement more complex scenarios as well:
- When selecting multiple tasks for Rendez Vous, all of those tasks must be performed by the same user.
- If one of the tasks in the list of Rendez Vous items has Four Eyes defined with another task, then all those items have Four Eyes with the other task.
- When 3 tasks each have Four Eyes with the other 2, then all three tasks must be performed by a different user.
Needless to say that the complexity of these scenarios may lead to configuration mistakes. The Case Designer allows making such "mistakes" during modeling. The CaseFabric Engine is more precise. When validating the model, the engine will recognize invalid configurations.
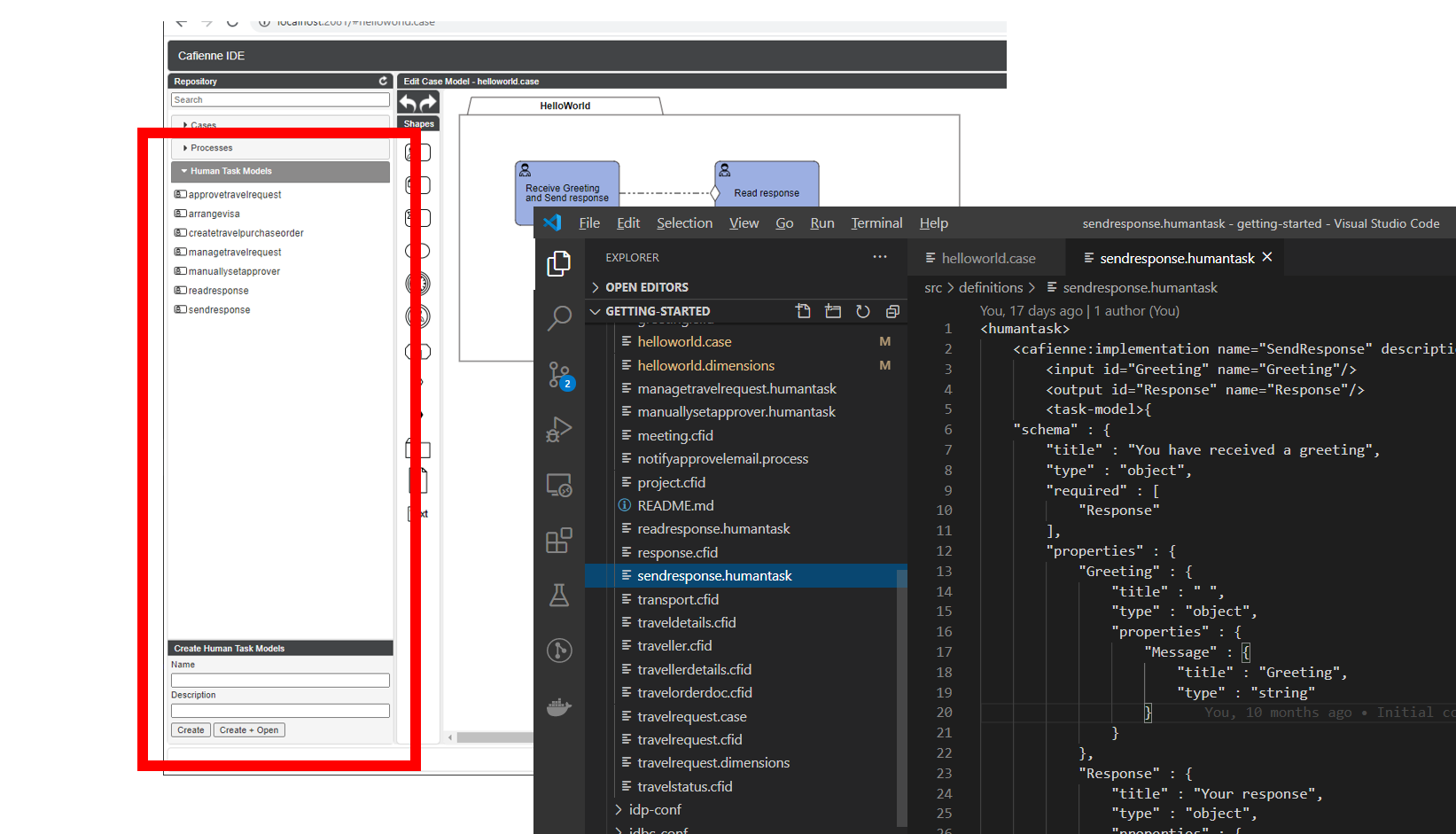
Reusable HumanTask implementations
The Repository Browser holds a list of independent Human Task implementations.
You can drag/drop them onto any case model in order to create a Human Task with that implementation.
The implementation of the Human Task is stored as a separate document with extension .humantask.
This enables fine-grained source control and reusability across other cases.
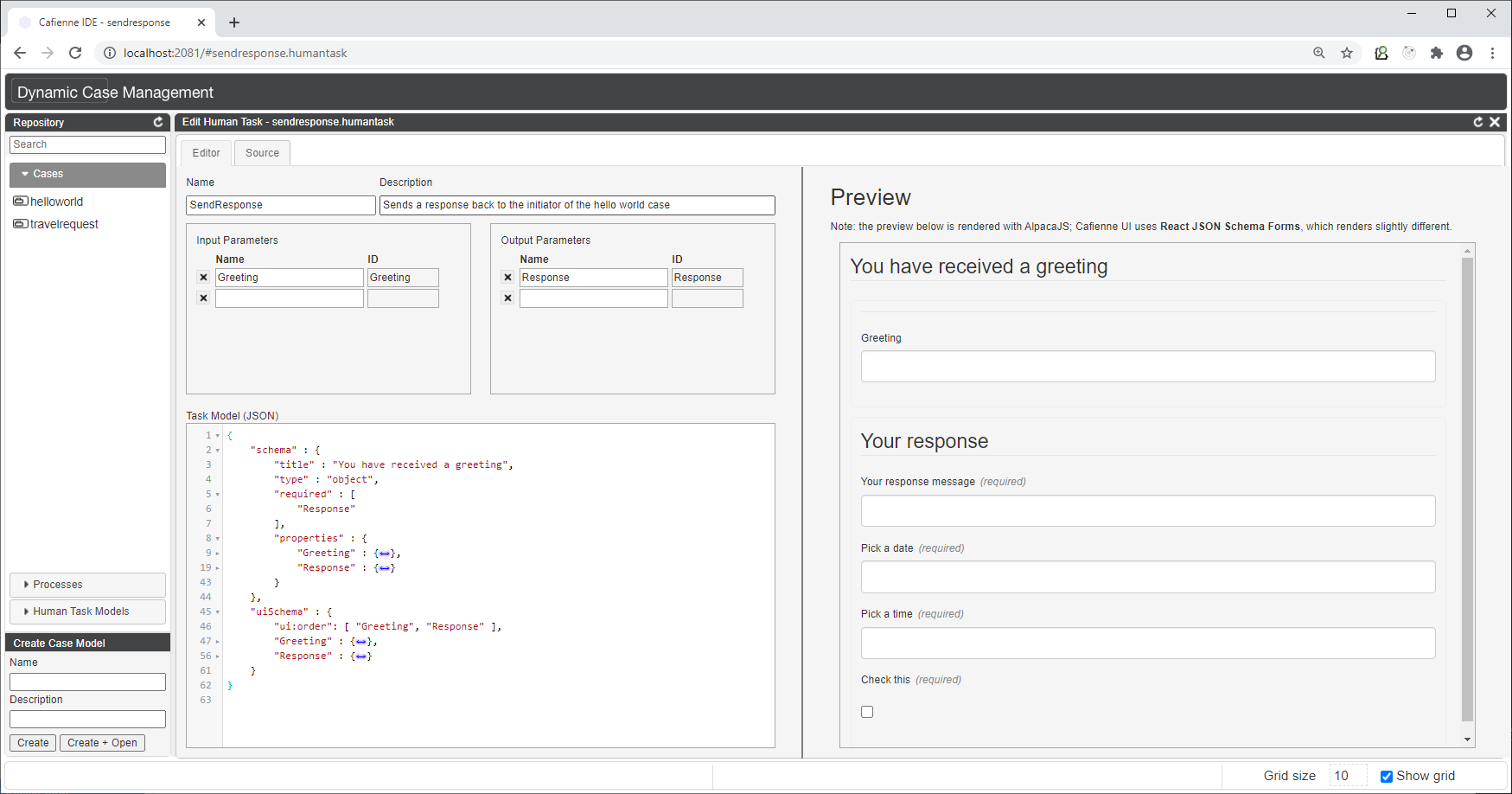
Form definitions for CaseFabric generic User Interface
The CaseFabric UI can be used to render any case modeled with Case Designer.
The CaseFabric UI renders Human Tasks with the help of 2 open source frameworks that can interpret JSON Schema.
Please visit their website for extensive documentation.
The format of the task model needs 2 properties
schemadescribing the data that must be rendereduiSchemaoptional rendering suggestions
Case Designer supports basic JSON validation and a simple preview of the form.
Note: CaseFabric Engine does not put any restrictions on the content of the task model.
The information is passed through the engine as a string and then gets stored into the query database.
Task Data - Saving, Validating & Completing
Next to completing a task, CaseFabric supports saving intermediate task output and output validation.

Saving intermediate task data
If a user does not yet want to complete the task, but needs to switch to a different context, a user interface component can decide to save the data as entered by the user. Next time the task is opened, the data is available to continue editing.
Furthermore CaseFabric Engine supports 2 additional features for validation before the task can be completed to ensure a that task output will not corrupt the case at hand.
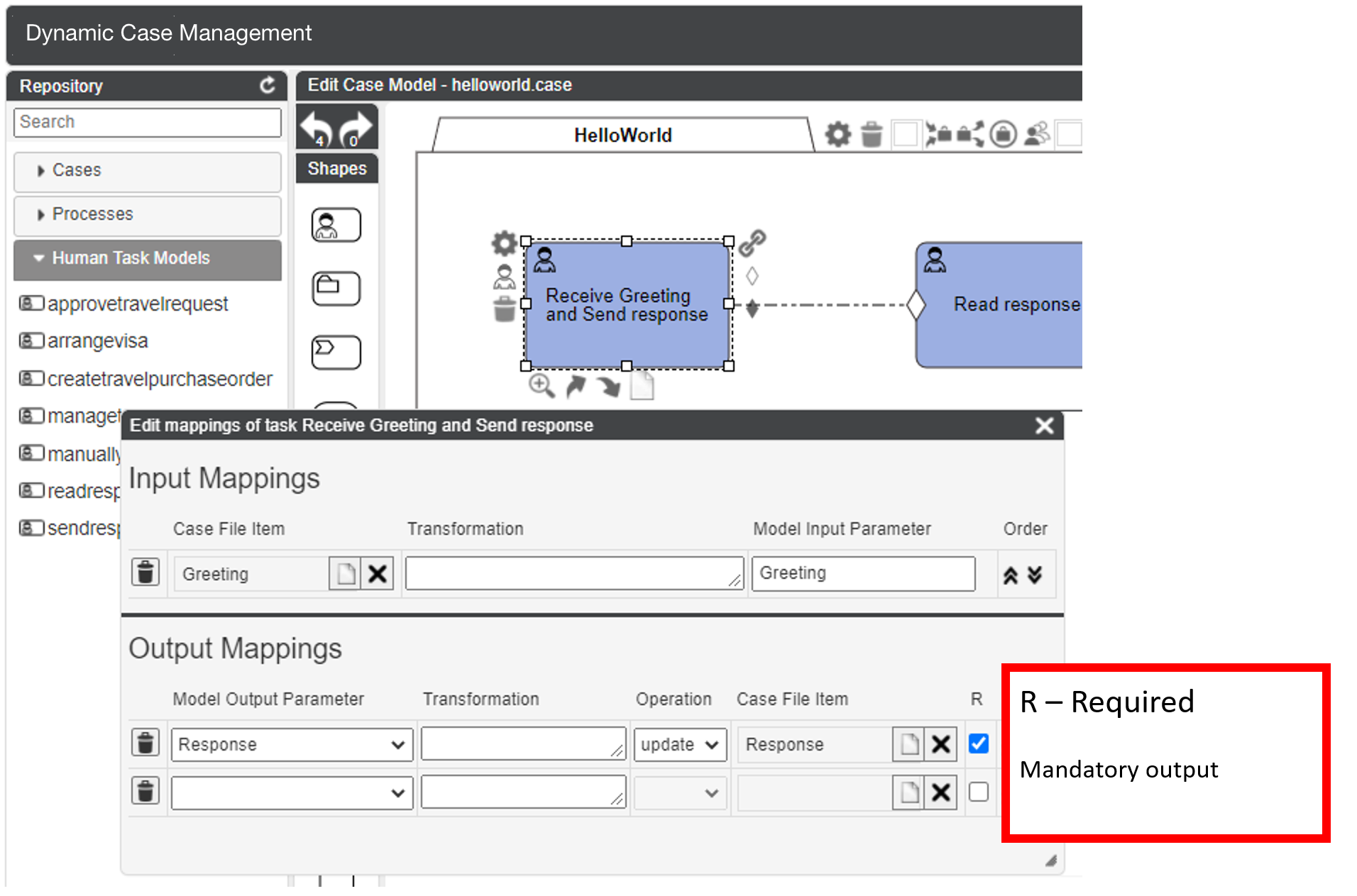
Mandatory output
When you open the input/output mappings of a Task, there is a small checkbox for output parameters,
titled R. With this checkbox, it is possible to mark an output parameter as required, making task completion validate that the parameter has a value.
If the parameter has no value, the task cannot be completed.
Intermediate validation
Note: task output validation is an experimental feature
CaseFabric Engine supports a new API call to enable validation of (potential) human task output. This can be used e.g. to validate a ZipCode or the existence of an email address in a database.
The current functionality is rather basic. The validator must be implemented as a REST service. The content to validate is posted to the CaseFabric Engine. The engine then invokes the REST service with that content.
- If the REST service returns without any content, it is considered valid, and CaseFabric Engine responds
202 Accepted. - If the REST service returns with some JSON, the content is considered invalid, but CaseFabric Engine also responds
202 Accepted, along with the JSON received from the service. - If the REST service is unavailable or returns an error, the CaseFabric Engine responds with
400 Bad Request.